The Role of Terminal Group Position in Triphenylamine Based Self-Assembled Hole-Selective Monolayers in Perovskite Solar Cells
Ece Aktas a, b, Rajesh Pudi a, Nga Phung c, Robert Wenisch d, Marion A. Flatken c, Iver Lauermann d, Antonio Abate c, e, Emilio Palomares a, f
a Institute of Chemical Research of Catalonia (ICIQ-BIST), Avinguda dels Països Catalans, 16, Tarragona, Spain
b Departament de Química-Física i Inorgànica. URV. E-43007. Spain., Campus Sescelades, Edifici N4, 2ona planta C/ Marcel.lí Domingo, 1, Tarragona, Spain
c Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialien und Energie GmbH, Kekuléstr. 5, Berlin D-12489, Germany.
d PVcomB/Helmholtz-Zentrum Berlin für Materialen und Energie, Schwarzschildstraße, 3, Berlin, Germany
e Department of Chemical, Materials and Production Engineering, University of Naples Federico II, Piazzale Vincenzo Tecchio, Napoli, Italy
f ICREA. Passeig LLuís Companys 23. E-08010. Spain.
Poster, Ece Aktas, 163
Publication date: 11th May 2021
ePoster: 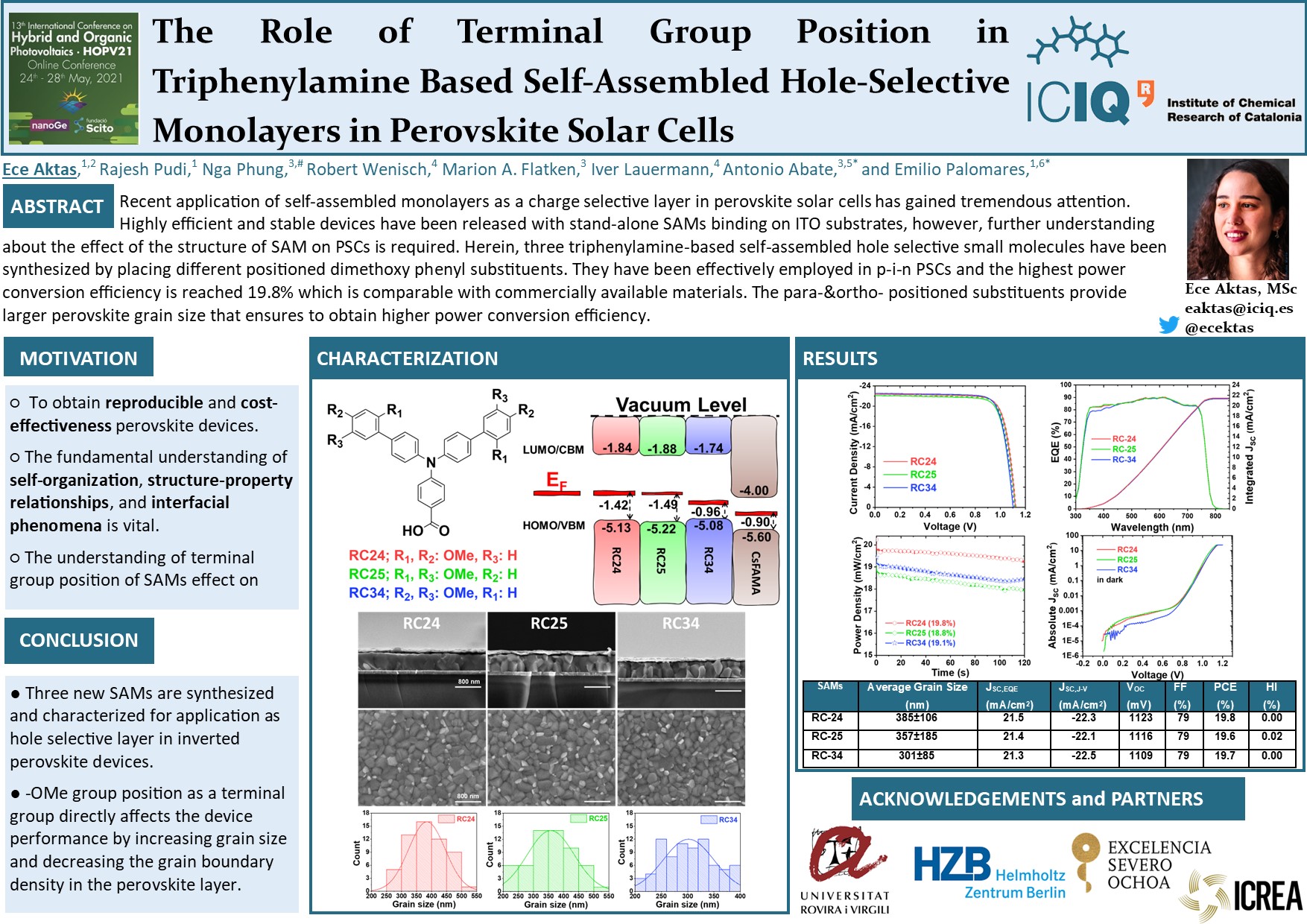
Recent application of self-assembled monolayers as a charge selective layer in perovskite solar cells has gained tremendous attention. Highly efficient and stable devices have been released with stand-alone SAMs binding on ITO substrates, however, further understanding about the effect of the structure of SAM on PSCs is required. Herein, three triphenylamine-based self-assembled hole selective small molecules have been synthesized by placing different positioned dimethoxy phenyl substituents. They have been effectively employed in p-i-n PSCs and the highest power conversion efficiency is reached 19.8% which is comparable with commercially available materials. The para-&ortho- positioned substituents provide larger perovskite grain size that ensures to obtain higher power conversion efficiency.
© FUNDACIO DE LA COMUNITAT VALENCIANA SCITO
